
How to Build Smart Cybersecurity Strategies to Protect Your Business
A cybersecurity strategy isn’t a simple how-to document; it is a well-thought-out plan that leads a business to sustainable and long-term success.

Content Map
More chaptersWhat defines strong security measures? Many believe it’s investing in fancy tools and training to raise security awareness among employees. Yet, all these would bring little to no result if you don’t have a strong cybersecurity strategy in place.
Cybersecurity provides organizations with a systematic approach amidst the chaos of constant cyber threats lurking on the horizon. It provides structure and focuses on safeguarding your business’s valuable data.
In this article, we’ll break down what a cybersecurity strategy is, why it’s essential, and how to create one from the ground up.
Key Takeaways:
- A cybersecurity strategy is a high-level document protecting a business’ digital assets.
- With cyber-attacks complex and continuously evolving, strict regulatory requirements, and remote working becoming an essential part of the work culture, businesses shouldn’t simply invest in tools but also in a strong cybersecurity strategy.
- Drafting a cybersecurity strategy requires an overhaul of the current data assets, strategic goal setting, assessment of the existing policies against the current cybersecurity landscape, and constant monitoring.
- It takes time and effort to draft a winning plan to safeguard your digital assets, so it’s best to consult with experts first.
Cybersecurity Numbers You Need to Know
Each year, experts say this year’s cybersecurity threats are worse than the last. In 2024, unfortunately, this statement still rings true.
- A Clark School study at the University of Maryland quantified the attack rate of computers with Internet access – every 39 seconds on average. In other words, the attack rate is nearly constant.
- IBM reported that in 2024, the average data breach cost was $4.88 million, a record high.
- According to Verizon, a non-malicious human aspect was present in 68% of breaches, such as a person making a mistake or becoming the target of a social engineering attempt.
- Gcore Radar Report highlighted that in the first half of 2024, the number of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) assaults increased by 46% over the previous year. Tech and gaming were the most affected sectors.
- Ransomware attacks have been increasing. In The New York Times article, large-scale ransomware assaults have become far more frequent. 2011 had 5 major attacks annually. 20 to 25 significant ransomware assaults occur daily in 2024.
- Cybersecurity incidents have become more costly in recent years, with financial losses quadrupling since 2017, according to the International Monetary Fund. While the majority of attacks result in relatively small losses, major incidents can lead to huge damage. Once every ten years, a company can face up to $2.5 billion in losses from a severe cyber attack. This underlines the importance of robust cybersecurity measures against the devastating consequences of cyber incidents.
- Major data breaches not only cause financial damage but also cause serious reputational damage. Examples of historical data breaches include:
- Ticketmaster: In 2024, 560 million Ticketmaster customers had information stolen in a massive breach.
- LinkedIn: In 2021, a breach exposed data of 700 million LinkedIn users, representing 93% of the platform’s members.
- Microsoft: In March 2021, Microsoft confirmed a breach affecting over 30,000 US organizations.
These statistics prove that the cyber threat landscape is constant and ever-changing. In a world relying on data, being proactive and taking measures to protect sensitive data is how you protect your business’s reputation and finances.
What Is a Cybersecurity Strategy?
It is a high-level plan that outlines how an organization protects its digital assets from evolving cyber threats. It establishes objectives, protocols, and responsibilities for preventing, detecting, and responding to security incidents while aligning with business goals. A strong cybersecurity strategy shifts from reactive to proactive measures, enabling continuous adaptation to emerging risks and ensuring critical data’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Regular reviews and updates keep the strategy effective in a dynamic threat landscape.
Why Do You Need a Cyber Security Strategy?
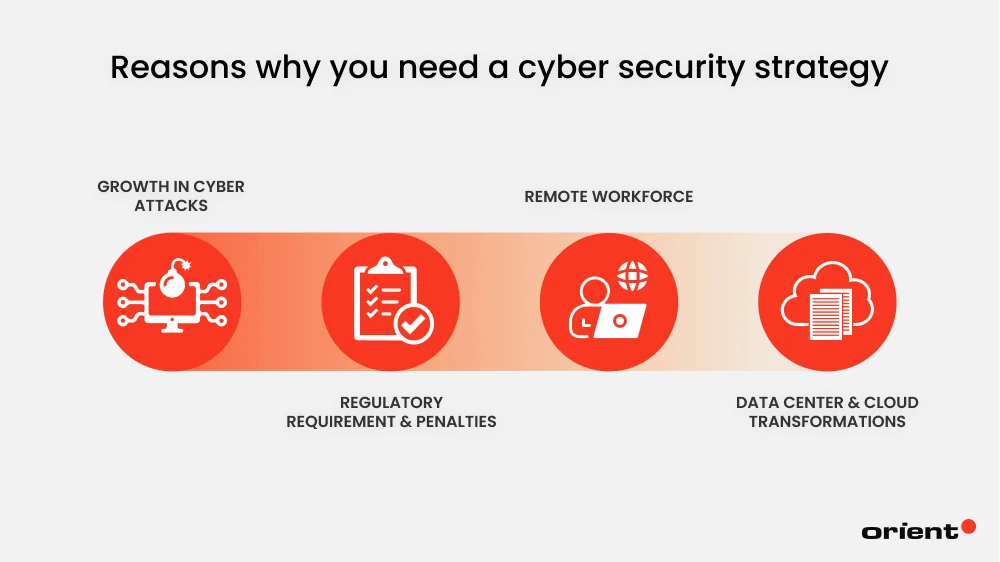
Growth in Cyber Attacks
In a world where everything is slowly digitizing, you must stay on top of such threats and protect sensitive data well. Statistics shown in the earlier section have proven that the number of attacks rarely goes down but rather constantly goes up.
There are several reasons behind the constant increase in cyber attacks. Cybercriminals are becoming smarter and utilizing technology like gen AI or deepfakes. There is also a lack of security awareness training in most organizations. The utilization of IoT (Internet of Things) with massive networks of gadgets has become the target of malicious attacks as IoT networks lack proper security safeguards.
Regulatory Requirement & Penalties
In an effort to safeguard digital assets, numerous regulations have been introduced, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the list goes on. Companies that fail to comply with these regulations or breach data face serious penalties. For example, under Article 83(5) of the GDPR, fines can go up to €20 million or 4% of a company’s global annual revenue from the previous year, whichever amount is higher.
Remote Workforce
The percentage of remote workers increased from 13% in 2020 to 28% in 2022. The pandemic played a large role in creating the shift from working in-office to working remotely. This working model is most likely here to stay since it offers multiple benefits like work-life balance, increased productivity, and reduced commuting time.
Still, working remotely presents a number of risks. Unsecured networks, phishing scams, storing data on personal devices, or the lack of cyber security awareness pose serious risks to the company’s security, especially if there is no proper strategy and policy in place.
Data Center & Cloud Transformations
Businesses have embraced cloud computing for years now due to its obvious benefits – cloud infrastructure is reliable, accessible, and scalable. Businesses don’t need on-premise infrastructure to enjoy all of these benefits. It’s no surprise that 74% of enterprises and 66% of small businesses are ready to adopt it.
However, similar to remote work, businesses need to have a strong cyber security strategy in place, as malicious malware, limited visibility into the network, and accounting hijacking are glaring problems in cloud transformations.
Considerations When Building a Cybersecurity Strategy
In the ever-changing digital landscape, the sheer number of threats can be overwhelming and paralyzing. Worry not, as even the most complex security problems have viable solutions.
Let’s begin by dissecting the main elements of a cybersecurity strategy and move on to the basic security policies to build the most comprehensive strategy for your company.
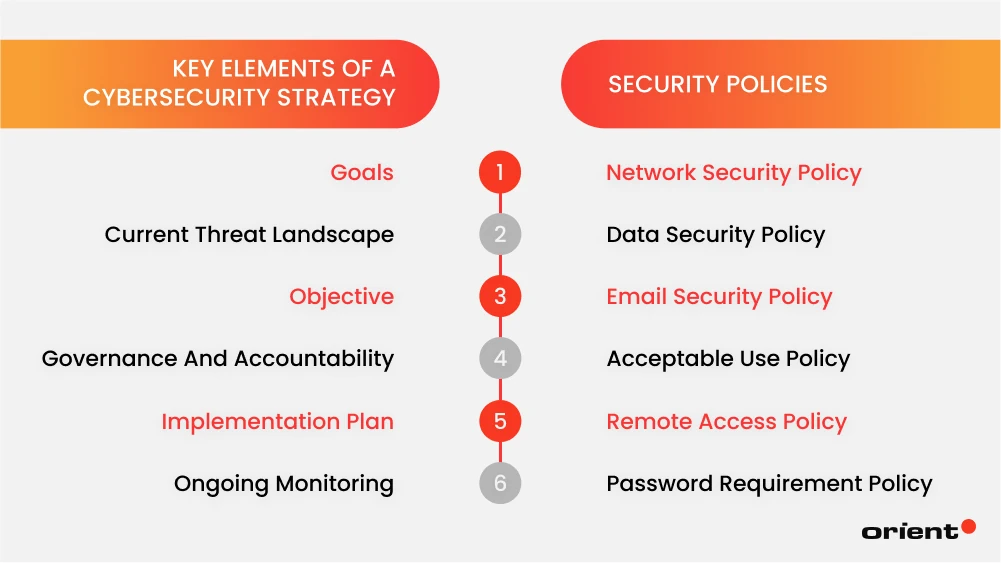
Key Elements of a Cybersecurity Strategy
Every successful cybersecurity strategy is made up of the following components:
- Goals: The strategy should state its fundamental objective to the stakeholders. For example, it aims to safeguard sensitive and confidential information and foster security awareness among employees.
- Current threat landscape: This section details the threats, vulnerabilities, and risks and their impact on the organization.
- Objective: Although goals and objectives are familiar, goals state the broader vision while objectives detail how the goal is executed. For instance, to reach the goal of enhancing employee’s security awareness, employees must complete training in a specified timeline.
- Governance and accountability: By specifying responsibilities in this section, the document promotes clarity and credibility.
- Implementation plan: This part spells out how each step is taken, addressing the administrative, technical, and physical aspects.
- Ongoing monitoring: The team needs to constantly monitor threats and look for ways to improve the existing cybersecurity strategy.
Security Policies
A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy is made up of one or multiple security policies. A cybersecurity policy is a set of guidelines that help organizations safeguard their digital assets by outlining rules for handling sensitive information, managing cyber threats, and ensuring regulatory compliance. It guides employees on acceptable device usage, data sharing, and responding to security incidents.
While having a single, overarching security policy is a great start, many businesses opt for multiple, specific security policies. Policies might vary depending on the business and the industry. The following is a list of sample policies and what they mean.
- Network security policy: This policy guides how an organization uses and manages network-based assets. This involves what constitutes appropriate network asset use, standardized security procedures, and other optimal measures to protect the network against threats.
- Data security policy: This policy outlines how an organization’s data is handled, stored, and maintained in a way that maintains the data’s integrity, availability, and confidentiality. This also encompasses the access, usage, or changes made to the data assets.
- Email security policy: As its name suggests, this policy guides how email systems should be used to protect the organization from malicious attackers, phishing, malware, etc. It may detail steps when employees receive a suspicious email.
- Acceptable use policy: This broad policy might involve acceptable or unacceptable use of Internet browsing/ social networks or the transfer of confidential information to protect employees and the organization from cyber-attacks.
- Remote access policy: The policy details rules and steps employees need to follow when they access the company’s asset and network remotely, e.g. what types of operating systems are permitted.
- Password requirement policy: This policy might define what a strong password is, how to create one and the frequency of changing it to safeguard data.
6 Steps to Build an Effective Cyber Security Strategy

There is no one-size-fits-all cyber security strategy. It depends on the company’s size, industry, and unique needs. Each strategy, therefore, should be customized. This is why we recommend consulting cybersecurity experts for the best outcome.
Still, there are six basic steps most strategy makers need to follow, and you can kickstart the security journey by following them.
Step 1: Security Risk Assessment
A security risk assessment draws the full picture of the threats a business faces, gaps in the current processes and policies, and the overall security posture. Since this assessment gives an organization the bigger picture, it helps identify and map its assets and data based on their value, as well as how resources should be allocated to implement the most effective cybersecurity strategy.
It’s easy to feel overwhelmed when the first step aims to achieve several things at once. It’s much easier to manage if you break down this large step into smaller ones.
- Identify assets. Leverage your current asset tracking system to determine the data classifications. This involves public data (e.g., website content), confidential data, intellectual property, internal use data, and data that needs to be strictly controlled to comply with regulations.
- Map assets. List everything regarding software, systems, users, and identity.
- Have a list or centralized database for all the approved software used in the organization.
- Leverage a Central Management Database (CMDB) and map all IT assets (like servers, devices, and networks) to their respective systems or owners.
- Group employees based on their roles or responsibilities (like HR, IT, or finance).
- Regularly review and ensure that employees only have access to systems or data that align with their current role.
- Understand the threat landscape. Understanding the threats your organization is likely to face is crucial. Not only taking factors like geographic location and type of infrastructure into consideration, but you should also examine contracts with third parties, identify a network’s connection to external infrastructure and how data flows within the organization.
- Prioritize risks. Identify core systems and owners, then track what systems or assets pose the highest threat to your business’ confidentiality and integrity.
Step 2: Establish Security Goals
Setting clear goals is the heart of any successful project or strategy. The same goes for cybersecurity strategies. Setting goals, however, can sometimes be tricky. If you don’t know where to start, here is a simplified walkthrough to set goals that lead your team to ultimate success.
- Align the goals with business strategy. How do the cybersecurity goals support your overall business goals? Cybersecurity should aim to help a business succeed sustainably.
- Identify critical assets. Concentrate on protecting the most valuable and sensitive data, systems, and processes.
- Assess your current cybersecurity posture. Benchmark your security posture against established frameworks like CIS or NIST or your industry peers to understand the business’ current capability.
- Understand compliance requirements. Keep the industry’s regulations in mind to ensure the strategy aligns with them.
- Evaluate available resources. Set realistic goals as there are budget, technology, and human resources limitations.
- Define roles and responsibilities. Assign teams to oversee the goals.
- Set a realistic timeline. Factor in external factors like vendor selection, hiring, or budget cycles when setting the timeline for the strategy.
Step 3: Assess the Level of Your Technology against Industry Best Practices
Technology develops in leaps and bounds, so it’s essential to evaluate your current technology to see if it meets the current best practices. Businesses need to stay up to date to protect themselves against the development of malicious actors.
Always start by assessing the current state of the operation system, then based on the goals in step 2, go through the system to check if there is any “technical debt” and handle it. Document each step strictly to keep track of any changes made.
Step 4: Review Existing Security Policies and Create New Ones
Earlier, we mentioned that a key consideration in cybersecurity strategies is security policies. In this step, the team should sit down together and double-check if the policies are still up to date and address emerging threats. Try to answer the following questions to determine if it needs to be updated or if a new one needs to be written:
- What policies are currently in use in the organization?
- Are these policies enforceable?
- Are they readily available for employees to view?
- Has the company conducted security awareness training for the employees to enforce the policies?
Step 5: Create A Risk Management Plan
Preparing for the worst is one way to stay proactive against security threats. This allows the organization to anticipate risks and come up with plans to deal with them before any damage takes place. Some actions you can take include:
- Create an incident response plan (IRP): Outline team roles, containment steps, and recovery processes for cyber incidents.
- Layered security: Use multiple defenses like firewalls, access controls, and endpoint protection to safeguard against breaches.
- Regular updates: Regularly update software or use automated systems to fix vulnerabilities.
- Create simulated attacks: Run phishing drills and cyber-attack simulations to test responses and improve training.
- Build a security culture: Promote security awareness through communication, updates, and rewards for safe behavior.
Step 6: Implementation & Evaluation
After careful planning and thorough evaluation, one of the last steps is to implement the plans to achieve the goals. In this step, administrative and technical teams need to work together to put the plan into action. This allows for the cybersecurity strategy to protect the organizations, prevent threats, and adopt new technologies along the way.
However, cybersecurity is not something that businesses can simply “set and forget.” It’s crucial to monitor, test, and update the system regularly based on business needs and new threats. It is recommended that you review and update the policies and strategies at least once a year.
Bring Your Cybersecurity Strategies to A New Level with Orient Software!

All in all, cybersecurity strategies take a lot of time and effort. Navigating complex regulations, multiple evolving threats, and constant governance can be overwhelming.
This is where Orient Software enters. Allow us to be your cybersecurity champion, lending a seasoned hand to secure your systems and safeguard your operations. Embrace your digital destiny with Orient Software—reach out today, and let’s rise to the challenge together!






