SOA and Microservices: Exploring the best choice of architecture for your business

Content Map
More chaptersIn the field of cloud computing, service-oriented architecture or SOA and microservices are well-known. A service-oriented architecture is a software design. On the other hand, a microservice is a distinctive architectural style for building applications and arranging them as loosely coupled services. The increase in the demand for highly scalable applications and the complexity of such applications have led to the developers adopting these architectures. The deployability of the applications with the use of any of these architectures is an added advantage. At first glance, the two architectures might sound similar; however, both are different from traditional architecture as they are scalable and comprise agile approaches. Let’s dive in further to look at the differences between SOA and microservices and find out the best strategy for your business.
What Is Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA)?

Service-oriented architecture (SOA) emerged to overcome the limitations of the monolithic architectures for the development of modern-day applications and their integration. The traditional architecture involved a complex procedure of connecting the application or functionality with other systems via point-to-point integration.
In SOA architecture, application components provide services to other components over the communication protocols in a network. Such communication is related to various services communicating with each other or a simple passing of data. The services in this context imply functions such as payment validation, account creation, or a simple provision of log-in. The protocols such as REST and SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) are used to interact with the services. Some of the critical services of SOAP are listed as below:
- Business services: These services comprise the business logic, information stored in the backend databases as well as the activity services. It can be represented using the XML language.
- Application services: The application service acts as the user interface through which other services can be invoked. They are confined to specific applications.
- Infrastructure services: These services perform non-functional tasks such as authentication, logging, and security. The services can be requested from the application services or the enterprise services. Infrastructure services can further be divided into subcategories such as communication services and utility services.
- Enterprise services: The enterprise services mainly depend on the application services and infrastructure services for performing business requests.
Why Service-Oriented Architecture?
The business infrastructure of an enterprise is diverse, consisting of multiple software systems and applications. This leads to a complex nature of business systems comprising of applications that are providing interdependent services. As a result, the modification and scalability of the technical infrastructure are crucial to meet the demands of the business. SOA has been able to address some of the critical challenges that the enterprises faced. SOA’s loosely coupled characteristics make it relatively simple to add on to new services as well as to upgrade the existing ones.
Some of the most common ones were the need for a quicker adaptability to business changes, support for newer channels for customer interaction. In addition, large-scale websites providing services on a web-based platform can gain a lot with the implementation of a service-based architecture. Here are some of the benefits of the service-oriented architecture that are outlined for a better understanding.

- Improvement in the flow of information.
- Flexibility in the functionalities.
- Reduced cost in the developmental cycle.
- Easy to manage.
- Improvement in data confidentiality and hence more reliability.
- Quicker system upgrades.
- Testing has improved.
- Reusability of codes.
- A standard form of communication is established.
- Allowing scalability to meet the needs of clients.
What is a Microservice Architecture?

Microservice architecture is another architectural pattern that divides large software into small components. In a microservice architecture, an application is built with various independent components. These groups of individual components run each application as a service. As a result, it is easier to scale applications built with this architecture and speed up the developmental process. There are four types of services under the microservice architecture.
- Functional service: Consists of services that help to perform business-specific operations. These services are not shared with other services and are externally accessible.
- Infrastructure service: These services are related to tasks such as auditing, security, and logging.
Why Microservice architecture?
The microservice architecture provides benefits over traditional architecture. As the services are divided into smaller components, they can be built by a smaller team. Microservices are used on a large scale, and it is evident from its demand by several businesses. The results achieved from the use of microservices have been productive. Let us explore the key features that have made microservices architecture preferred extensively.

- Scalable: The applications built using this architecture are simpler and can be alterable and scalable as per the changing business needs. There is no requirement of scaling all components together under this architecture.
- Independent components: Microservice architecture consists of independent components, thus making them easily upgradeable.
- Reduce developmental time: Each developer in the development phase can work independently, and it speeds up the process while reducing the developmental time for building the application.
- Frequent upgrades: The release of software through development, testing, and approval, allows regular updates thus keeping the applications to remain upgraded.
- Developmental freedom: The focus of a microservice architecture is to have the right tool for a concerned job. This implies that there is no standard pattern for the developers to follow, and they have the freedom to choose the best and effective tool for their problem.
- Agile: There is a possibility for a new feature to be quickly developed as well as discarded when not in need.
- Deployment: All microservices can be developed and deployed independently in any application.
- Technology: Various languages and technologies can be used to build separate services within the same application.
- Application functionality: The system will continue to function even at the failure of one of its services in the application.
Monolith vs. Microservices
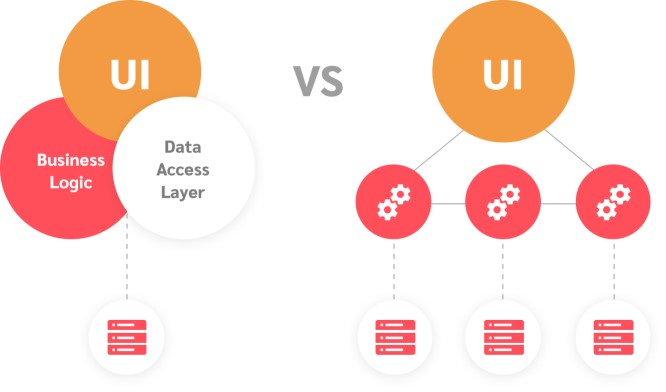
Monolithic architecture is the default approach for creating a software application. However, the trend of using a monolithic approach is reducing since it faces numerous challenges, such as scaling, implementation of changes or deployment as most of the applications that were developed under this architecture comprised of a huge code base. On the contrary, this trend is shifting towards adopting the SOA and microservices. Businesses prefer microservices as they offer tangible benefits in terms of scalability, agility, and flexibility, to name a few. Tech giants such as Google and Amazon are some well-known corporations that have successfully transitioned from a monolithic architecture to a microservice architecture for their business operations. This has made many companies follow in their footsteps of using microservices for efficiency in their business. The following section highlights the strengths and weaknesses of these architectures.
Monolithic
Strength of monolithic architecture
- Concerned with one application thus it is easier to manage.
- Debugging and testing of traditional architectures is easier as it is concerned with a single application.
- Easier deployment.
- The development of an application with the use of a traditional approach is much simpler.
Weakness of monolithic architecture
- Involvement of complex coding.
- Difficulty in the implementation of changes as a simple code change can affect the entire system.
- Independent scalability is not possible.
- Newer technical addition is problematic as it will require the application to be rewritten.
Microservice
Strength of microservice architecture
- Services can be independently deployed.
- Failure of service in an application does not affect the entire application.
- Easier to manage with simpler individual components.
- Scalability is one of its primary advantages. Cost-efficiency in business system development.
Weakness of microservice architecture
- It is complex to set up the connections between the databases and other modules involved.
- It comprises a distributed system, so the management of it can be tricky.
- Need for extra configuration, health checks, and logging.
- Testing multiple independent deployments can be difficult.
SOA vs. Microservices - Which one should you choose?
Both of SOA and microservices have their benefits, so the question lies in choosing the right one. Although they have their similarities, it is important to note the difference between microservices and SOA for a clearer understanding of the choice of architecture.

- Granularity: The architecture is made of several components and their granularity can be an important factor. Microservice architecture has smaller components than an SOA, which has lesser but bigger components and is not finely grained.
- Fault Tolerance: An enterprise service bus (ESB) performs various functions such as routing, protocol transformation, acts as the security gateway, etc. If any of these functions become faulty, it will block the request for that particular service. ESB can be a single point of failure under a service-oriented architecture that can affect the functioning of the complete application. In comparison between microservices and SOA, microservices architecture consists of services that are independent of each other in functioning and deployment, thus making this architecture fault tolerant, unlike SOA.
- Storage: Microservices have separate data storage for each service. These services can access independent storage. The services under SOA share the storage.
- Developmental teams: Under SOA, communication is shared among the groups. There can be a smaller team working independently for microservices, which is not interfered with by other services in its development and deployment.
- API layer and the messaging middleware in SOA: SOA comprises the messaging middleware, which is responsible for routing, protocol transformation, etc. Microservice architecture has the API layer that helps in the communication between the consumers and the service.
Large organizations offering heterogeneous services are inclined to service-oriented architecture (SOA) due to the possibility of integration among these services and the messaging protocols. On the other hand, smaller businesses, including web-based and mobile-based applications, do not require robust communication among the services provided. Microservice architecture is better suited for such business requirements.
Conclusion

It will not be accurate to conclude between SOA and microservices by saying a particular architecture is better than the other. Both these architectures have their advantages and disadvantages. It is mainly dependent on how diverse is your application environment. For example, the complicated business requirements will be better served using of service-oriented architecture, whereas microservices will be suitable for web-based services and a smaller business environment setup. Thus, the debate over SOA vs. microservices can be concluded by describing that the application will be the deciding factor over the choice of architecture in an enterprise.






