
The Journey of Software Reengineering: Resurrect, Refine, Revolutionize

Content Map
More chaptersIn the ever-evolving realm of technology, software reigns supreme. But what happens when your once cutting-edge software starts to lose its luster? Even if you’ve developed the best software of its time, there’s always room for improvement.
Welcome to the captivating journey of software reengineering - a process that allows you to resurrect, refine, and revolutionize your existing software.
Software reengineering is not just a luxury; it’s a necessity in today’s dynamic business landscape. As technologies advance, user expectations soar, and market demands evolve, staying ahead of the curve becomes paramount. By embracing software reengineering, you can enhance performance, scalability, and efficiency, ensuring your software remains competitive and aligned with changing industry standards.
What is Software Reengineering?
Software reengineering is a transformative process that aims to enhance and update legacy systems to meet present and future requirements. It is a complex undertaking that involves analyzing, redesigning, and modifying the software to address limitations, improve performance, and align it with changing business needs. Therefore, software engineers for this role should necessitate a comprehensive understanding of the software system’s design, architecture, and functionality.
The software reengineering process encompasses key steps such as reverse engineering, restructuring, and forward engineering. These steps empower software engineers to identify and resolve issues within the legacy system and upgrade it to meet present and future demands.
At its core, software reengineering projects are the practice of revitalizing and rejuvenating software that has become outdated or no longer meets current requirements. It involves a comprehensive evaluation of the software architecture, source code, and functionality to identify areas for improvement. Through systematic analysis and modifications, the goal is to enhance the software’s performance, maintainability, and scalability.
Software reengineering is distinct from other software engineering process approaches, such as new development or maintenance. While new development involves creating software from scratch and maintenance focuses on fixing bugs and making minor updates, reengineering centers around transforming and optimizing existing software. Re-engineering harnesses the foundation of an already functional system, giving it a new lease on life through strategic modifications and enhancements.
The Benefits of Software Reengineering for Businesses
A software reengineering project offers numerous benefits that directly impact businesses’ operational efficiency, competitiveness, and growth.
- Improved Performance: Reengineering allows businesses to optimize software performance, enhancing response times, reducing bottlenecks, and increasing overall efficiency. It enables applications to handle larger workloads and scale effectively.
- Enhanced Maintainability: Outdated software often becomes challenging to maintain and support. Through reengineering, businesses can streamline and simplify the software’s structure, making it easier to understand, update, and maintain over time.
- Adaptability to Changing Needs: Business requirements evolve, and software must keep pace. Reengineering enables businesses to align their software with current needs, incorporating new features, technologies, and integrations to meet evolving market demands.
- Cost Savings: Replacing an entire software system can be costly. Software reengineering offers a cost-effective alternative by leveraging existing investments and incrementally improving the software’s functionality, reducing the need for a complete overhaul.
- Competitive Advantage: Upgrading and modernizing software through reengineering equips businesses with a competitive edge. It allows them to offer enhanced user experiences, improved performance, and innovative features that set them apart from their competitors.
Software reengineering holds the potential to transform underperforming software into a valuable asset for businesses. By breathing new life into existing systems, optimizing performance, and adapting to changing needs, reengineering empowers businesses to stay agile, efficient, and competitive in today’s technology-driven landscape.
The Signs of Needing Software Reengineering
Recognizing the signs that indicate the need for software reengineering is crucial to ensure that your software remains efficient, reliable, and aligned with your organization’s goals.
Legacy Software Reengineering or Compatibility Issues with Existing Systems
One of the clear signs that a software system may need reengineering is when it becomes outdated or incompatible with modern technologies. Legacy software, built on outdated platforms or using obsolete programming languages, may struggle to integrate with newer systems or have an inconvenient user interface. In such cases, software reengineering becomes necessary to update the system and ensure compatibility with the latest technologies.
Performance and Scalability Limitations
If a software system experiences performance bottlenecks, frequent crashes, or slow response times, it indicates the need for reengineering. As businesses grow and user demands increase, software systems must be capable of handling larger workloads and scaling effectively. If the existing system struggles to meet performance requirements or lacks scalability, reengineering can optimize the software architecture, improve algorithms, and enhance resource management to deliver better performance and scalability.
High Maintenance Costs and Frequent System Failures
Legacy systems often require extensive maintenance efforts and incur high costs due to their outdated infrastructure, complex codebase, and lack of support from vendors. If a software system demands frequent fixes, patches, and updates, and the associated maintenance costs become unsustainable, it may be a sign that reengineering is needed. By reengineering the software, companies can streamline the codebase, eliminate technical debt, and reduce the ongoing maintenance burden, resulting in cost savings and improved system stability.
The Journey of Software Reengineering Process
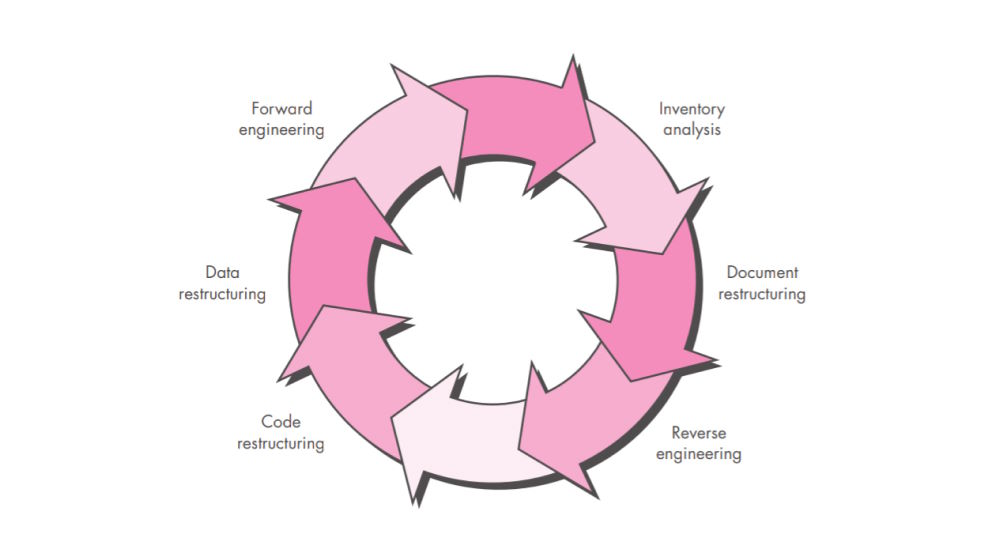
The software reengineering process can indeed be broadly categorized into three main phases: reverse engineering, restructuring, and forward engineering. These phases work together to enhance and modernize existing software systems. Let’s explore each phase in more detail.
Phase 1: Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering entails examining and comprehending the current software architecture. It aims to gain insights into the system’s architecture, design, and functionality. Here are some key aspects of reverse engineering:
- Code Examination: Developers examine the source code, documentation, and other available resources to understand how the software works. They analyze the code structure, algorithms, and patterns used in the system.
- Documentation Review: Existing documentation, such as system specifications, user manuals, and design documents, is reviewed to gather information about the system’s intended functionality and design decisions.
- System Analysis: Developers analyze the system’s behavior, data flow, and interactions with external components. They may use tools to visualize the system’s structure, identify dependencies, and trace the execution flow.
The primary goal of reverse engineering is to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the existing software system. This knowledge helps identify areas for improvement and lays the foundation for the subsequent phases.
Phase 2: Restructuring
The restructuring phase focuses on redesigning and reorganizing the software system to enhance its performance, maintainability, and scalability. Here are the key aspects of the restructuring phase:
- Code Refactoring: Developers modify the existing codebase to improve its structure, readability, and maintainability. This may involve removing duplicate code, extracting reusable components, and applying design patterns to enhance the system’s modularity.
- Architecture Enhancements: The system’s architecture may be redesigned to address architectural flaws, improve scalability, or incorporate new technologies. This includes reevaluating component interactions, introducing layers or modules, and optimizing system performance.
- Removal of Obsolete Code: Outdated or unused code is identified and removed, reducing complexity and improving system performance. This declutters the codebase and makes it easier to understand and maintain.
The restructuring phase aims to optimize the software system’s structure, making it more efficient, flexible, and maintainable. It addresses identified weaknesses and prepares the system for future enhancements.
Phase 3: Forward Engineering
The forward engineering phase involves using the knowledge gained from reverse engineering and the improvements made during the restructuring phase to develop a new and improved version of the software. Here are key aspects of forward engineering:
- Implementation of Redesigned Components: Developers implement the redesigned or refactored components based on the insights gained from reverse engineering and restructuring. This may involve rewriting code, introducing new libraries or frameworks, and integrating modern technologies.
- Introduction of New Features: The re-engineered software may include new features or functionality to meet updated business requirements. This involves designing and developing additional modules or modules with enhanced capabilities.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing is conducted to ensure that the reengineered software meets the defined requirements and functions as intended. This includes various testing techniques, such as unit testing, integration testing, and system testing, to validate the system’s stability, reliability, and performance.
The forward engineering phase culminates in a new version of the software that incorporates the insights gained from reverse engineering and the improvements made during restructuring. The re-engineered software is now ready for deployment and use.
By following these three phases of reverse engineering, restructuring, and forward engineering, the software reengineering process allows businesses to breathe new life into their existing systems. It enables them to optimize performance, enhance maintainability, and align with modern requirements, ensuring the system remains robust and adaptable in the face of evolving business needs.
Choosing the Right Partner for Software Reengineering
When embarking on a software reengineering project, selecting the right partner is crucial to ensure its success. One reputable software reengineering partner to consider is Orient Software. We are known for our expertise and experience in delivering high-quality software development services.
Orient Software brings extensive expertise and experience to the table. We have a team of skilled professionals who specialize in software reengineering and possess in-depth knowledge of modern technologies, programming languages, and software development best practices. Their experience in handling diverse reengineering projects equips them with the insights and capabilities to effectively address the unique challenges that may arise during the process.
Furthermore, it is beneficial to consider Orient Software’s approach to collaboration and communication. Effective communication and collaboration are vital for a successful partnership, ensuring that the reengineering process remains transparent, efficient, and aligned with the client’s objectives. Orient Software emphasizes open and frequent communication, fostering a collaborative environment that promotes shared understanding and enables effective decision-making throughout the project.
By evaluating the capabilities and reputation of potential service providers like Orient Software, businesses can make an informed decision and establish a partnership that sets the stage for a successful software reengineering project.






