
V-Model (Software Development): A Comprehensive Handbook
Content Map
More chaptersSoftware development is an intricate and long process. This is why numerous software development models have been built to accommodate a broad array of needs, project sizes, demands, and experience. The waterfall model, agile model, and spiral model are some of the names among these models.
In today’s article, we are going to delve into the V model. This article will cover what the V model is, its phases, core principles, and why or why not a team might choose this model in software development.
Key Takeaways:
- V Model is a systematic software development approach that highlights early testing and extensive documentation.
- Shaped like a V, this model has a testing phase corresponding to each development phase.
- It consists of two phases: Verification (product development) and Validation (testing).
- Since the V model takes a structured and sequential approach, it is best suited for projects with set and clear requirements.
What Is the Meaning of the V Model in Software Development?

The V-Model, known as the Verification and Validation Model, is a structured software development approach that emphasizes early and thorough testing throughout the software development life cycle. Its name comes from its V-shaped visual structure, where development phases (like requirements and design) on the left side are matched by corresponding testing phases (like unit and system testing) on the right side. Each development stage has a paired testing activity, ensuring bugs are detected and resolved early, which leads to higher-quality software, faster development, and lower costs.
Phases of V Model in Software Development
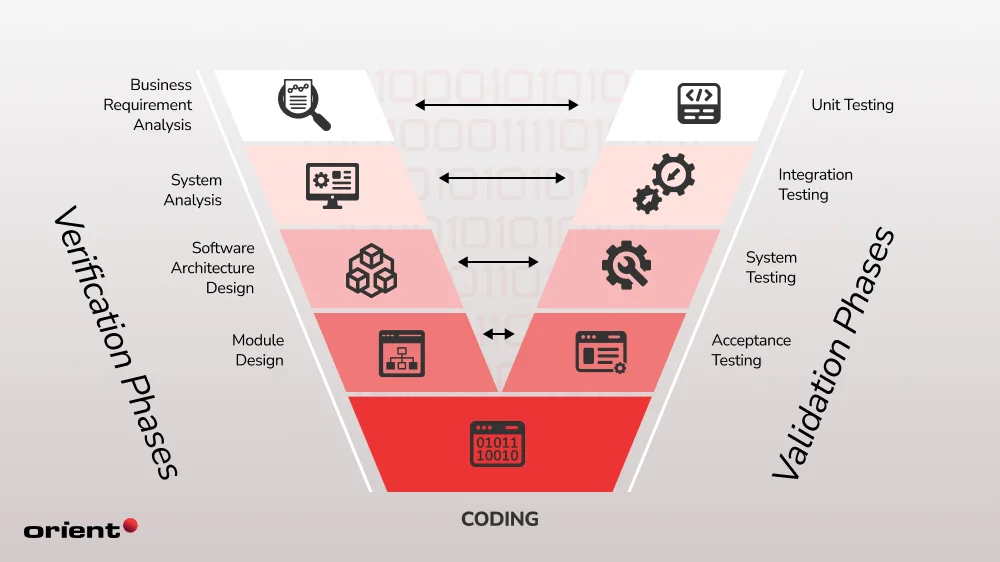
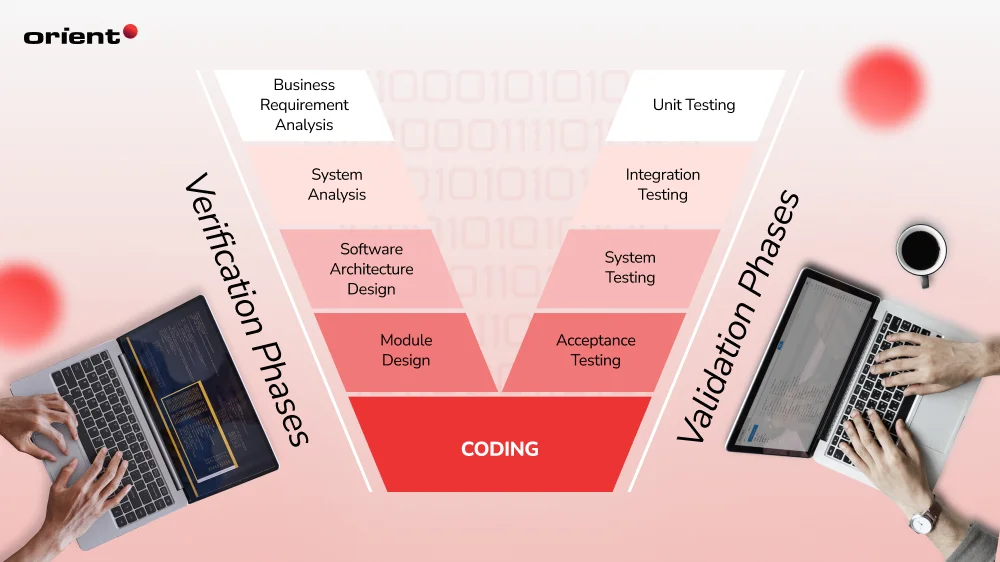
The V model consists of 2 main phases: Verification and Validation. Starting at the top left corner of the V-shaped model, the software development process moves to the right side to its corresponding testing phase. With the clear testing requirements at each development stage, this model makes sure team members are collectively moving towards the project’s objectives and goals.
Verification Phases
The verification is typically on the left side of the V-shaped model. It involves product development stages and the process evaluation to ensure the requirements are met. This phase often is static analysis and aims to answer the question of “Does the delivered product meet the requirements and specifications?”
The verification phase can be broken down into five smaller stages:
Business Requirement Analysis
Before the actual work starts, the team needs to understand the customer requirements thoroughly. Most customers have a vague idea of what they want, so proper communication to understand their needs and expectations is paramount.
After a thorough conversation with the customers, the gathered information needs to be refined and rewritten into clear, consistent, and unambiguous requirements and put in the user requirements document. This document should spell out all the functional and non-functional requirements as well as any priorities that the team needs to pay special attention to.
System Analysis
The next step is to interpret the user’s requirements. System engineers and the development teams discuss the requirements and convert them into product features. The system design step typically involves hardware requirements, needed resources, and any additional communication to set up the product development.
Software Architecture Design
Software architecture is chosen based on a number of criteria: the list of modules, their brief functionality, interface relationships, dependencies, relationships, database tables, technological details, and the list goes on.
This overall high-level design enables the design and documentation of integration tests.
Module Design
While software architecture is a high-level design, the module design is considered a low level design. To be specific, a detailed internal design of the modules is developed. Factors like its compatibility with external systems, how the data is collected and integrated, and so on are all carefully considered in this phase. Based on all this information, unit tests may be developed simultaneously.
Coding
The detailed module designs are taken up in the coding phase. Based on the designs of the previous steps, the development team selects the most suitable programming language. A coding standard and principle must be followed at this stage. The codes go through careful review and checking before being checked into the repository.
Validation Phases
The validation phase is on the right side of the V shape. While the verification phase makes sure the requirements are met, validation phases use dynamic analysis techniques, meaning it involves both functional and non-functional testing to guarantee that the product meets customer requirements and expectations. The validation phase can be broken down into four smaller tests.
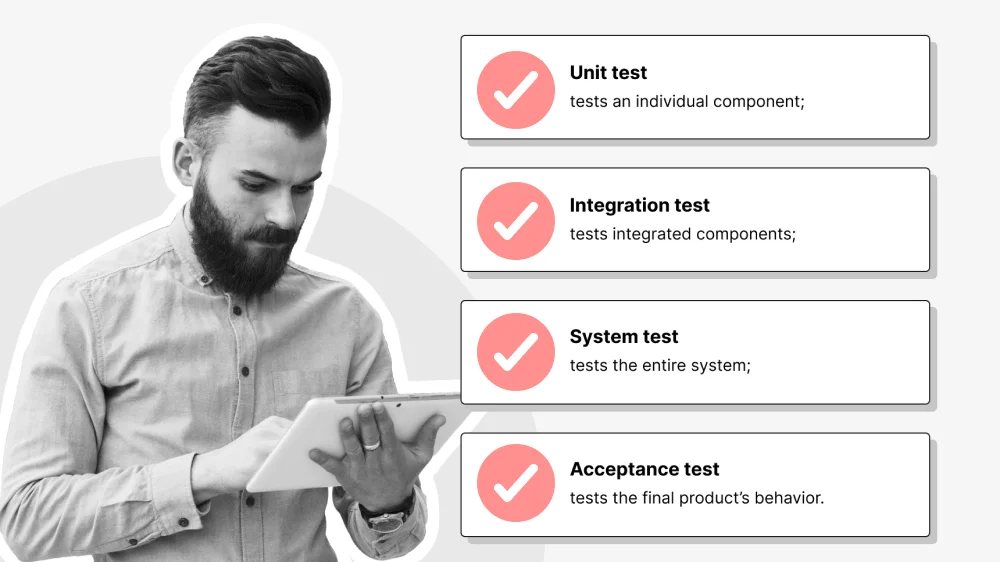
Unit Testing
In the V model, unit testing corresponds to the module design phase. Also referred to as component test execution, this type of test is run to identify any bugs or errors at the unit level. The test is conducted on the smallest entities, like modules, objects, or classes. These elements are tested in isolation from the system to make sure they work properly. Defects are typically fixed as soon as they are detected.
Integration Testing
Corresponding to the system analysis stage, integration testing is performed to certify the communication between the modules. To be specific, teams review how modules are integrated and how the data is passed through interfaces. Integration testing aims to check and see if the independently tested groups can coexist and communicate with one another.
System Testing
System testing happens during the system design stage. This test is done by the client’s business team. The main aim of this stage is to go through the entire system, as well as functional and non-functional test cases, to make sure every business requirement is met.
Acceptance Testing
This is related to the business requirement analysis part of the V-model. It is performed in the user environment and verifies if the product has any compatibility issues with different systems. This test is used to test non-functional problems like load time or performance. In short, acceptance testing is used to see if the product is ready for the real world.
Key Principles of the V Model

There are five core principles teams need to keep in mind when it comes to the V model.
- Integrate Testing Throughout Development: Testing is not an afterthought or the final step in the software development process. It’s included from the early stages of requirement gathering to the deployment phase. This proactive approach helps maintain software quality from start to finish.
- Plan Testing in Parallel with Development: Each development phase has a corresponding testing phase. This parallel approach optimizes resources and ensures testing is ready when needed, so concurrent planning is essential.
- Prevent Defects: Prevention is better than cure. The V model highlights the importance of problem prevention rather than detecting and fixing them later. Teams can save time, resources, and foster smoother development by preventing late-stage fixes.
- Develop Clear and Concise Requirements: As the V model constantly gathers, reviews and refines requirements, it underscores clear and concise demands to create the highest quality application possible.
- Combine Development and Testing: Even though the V shape has two distinct sides, its development phases and testing phases are closely interconnected. This tight feedback loop can drive better software outcomes.
Strengths and Weaknesses of the V Model

Similar to other software development models, the V model consists of strengths and weaknesses.
Strengths
- Improved software quality: As a highly disciplined model, where phases go one by one, the V model offers better quality as it emphasizes early and continuous testing.
- Lower defects: The proactive approach of the V model enables the early detection of bugs and errors, minimizing risks and problems.
- Better project management: This model’s clear and structured approach enables easy planning, resource allocation, and process tracking.
- Clear documentation: The clear and structured approach of the model comes with extensive documentation, which guides the team and maintenance and development efforts.
- Stronger communication and collaboration: The model encourages constant communication between developers, testers, and relevant stakeholders.
- Improved resource optimization: With the concurrent planning of development and testing, resources are utilized more efficiently.
Weaknesses
- Rigid: Being highly structured means the V model isn’t accommodating to changes. Adjustments during the later development stages, especially, may cause costly delays.
- Time-consuming: Deadline-driven projects might not be suitable with the V model as the focus on extensive testing and documentation may extend project timelines.
- Resource-intensive: Although planning in the V model can optimize resources, it still requires dedicated resources, which may not be suitable for small teams.
- Less agility: The rigid approach of the V model makes it difficult to incorporate continuous feedback and make iterative improvements.
- Not suitable for complex projects: The V model may struggle to adapt to projects with uncertain or evolving requirements.
- Delayed prototypes: With a heavy focus on structured developmental stages, working prototypes may not be available until later stages, which may delay the validation and stakeholder feedback.
When to Use the V Model?

The V model has a clear and structured approach to the software development process. However, this strong point might also be its weakness. Hence, the V model is suitable when:
- There are clear and set requirements. Since the V model is quite rigid and takes a sequential approach, it is best fitted for projects that don’t require much flexibility.
- The project is high-risk. The thorough testing of the V model ensures no major bugs are detected in the later development stages.
- The project has strict compliance requirements. Industries like healthcare or defense have strict regulatory requirements and standards. V model’s thorough testing and documentation are extremely beneficial in these cases.
- The project is small or medium-sized. Moderate complexity allows the team to carefully develop and test the software step by step.
Conclusion
The V Model’s structured approach shines in industries like finance, healthcare, and government, where precision and thorough documentation are paramount. Though it may be less flexible than other methodologies, its comprehensive testing ensures top-notch quality and reliability, making it a trusted choice for high-stakes projects.
If you’re intrigued by the V Model but unsure if it’s right for you, let Orient Software guide you! With two decades of expertise across various development models, we’re confident we can help you find the perfect fit for your project’s needs. Contact us today, and let’s get started!






